CCNA Chapter 1: Networking Fundamentals
What is Networking?
Networking connects computers and other devices to share data and resources. It forms the foundation of communication from small homes to enterprise and internet-level connections.
OSI Model (7 Layers)
The OSI model is a conceptual framework that standardizes network communication into 7 distinct layers:
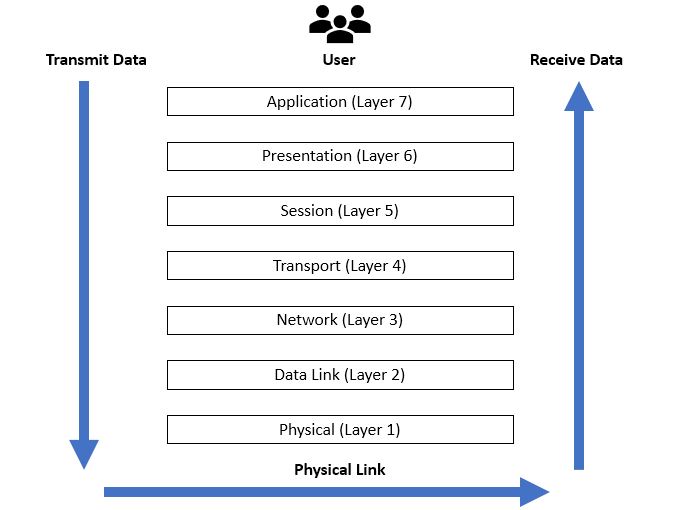 View Full Image
View Full Image
| Layer | Name | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | Application | User interface and network services |
| 6 | Presentation | Data encoding, encryption |
| 5 | Session | Session control and maintenance |
| 4 | Transport | TCP/UDP, reliability, flow control |
| 3 | Network | IP addressing and routing |
| 2 | Data Link | MAC addressing and frame forwarding |
| 1 | Physical | Cabling, signals, physical media |
TCP/IP Model
The TCP/IP model simplifies the OSI model into 4 layers used in real-world networking:
| TCP/IP Layer | Corresponding OSI Layers |
|---|---|
| Application | 7, 6, 5 |
| Transport | 4 |
| Internet | 3 |
| Network Access | 2, 1 |
Network Topologies
- Bus: All devices share a single communication line.
- Star: Devices connect to a central switch or hub.
- Ring: Devices form a closed loop with data passing in one direction.
- Mesh: Every device connects to every other for redundancy.
Ethernet Standards
| Standard | Speed | Media |
|---|---|---|
| 10BASE-T | 10 Mbps | Cat3/Cat5 |
| 100BASE-TX | 100 Mbps | Cat5 |
| 1000BASE-T | 1 Gbps | Cat5e/Cat6 |
| 10GBASE-T | 10 Gbps | Cat6a/Cat7 |
IP Addressing: IPv4 and IPv6
IPv4: 32-bit addresses written as four octets, e.g. 192.168.1.1.
Classes:
- Class A: 1.0.0.0 – 126.255.255.255
- Class B: 128.0.0.0 – 191.255.255.255
- Class C: 192.0.0.0 – 223.255.255.255
Subnetting: Divides networks into logical segments to optimize traffic.
IPv6: 128-bit addresses, written as hexadecimal, e.g. 2001:0db8:85a3::8a2e:0370:7334.
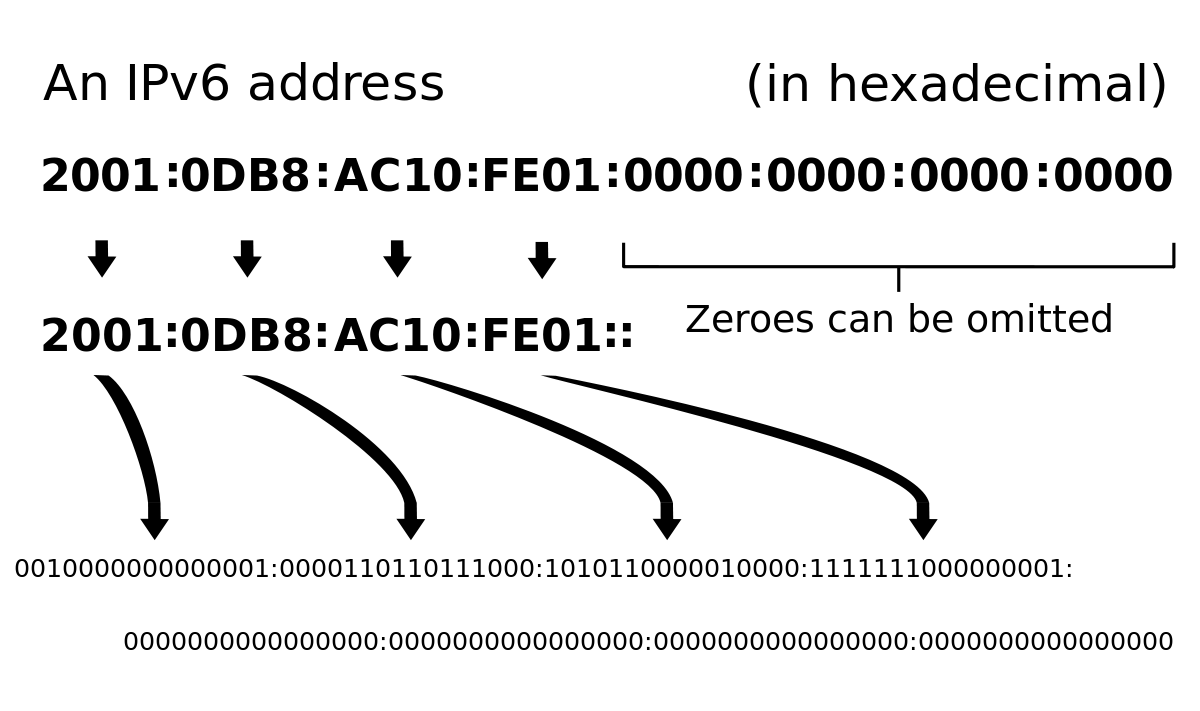 View Full Image
View Full Image
- Global Unicast: Routable on the public internet
- Link-local: Used for communication within a local segment
- Multicast: One-to-many communication