CCNA Chapter 2: Network Access
Switching Concepts
Switches are intelligent Layer 2 devices that forward Ethernet frames using MAC addresses. They reduce collision domains and improve network efficiency.
📘 Exam Tip: Remember that switches operate at Layer 2 but can also perform Layer 3 switching (multilayer switches).
- Store-and-forward: Entire frame is checked for errors before forwarding.
- Cut-through: Faster, but forwards possibly corrupted frames.
Command Example:
Switch(config)# mac address-table static aaaa.bbbb.cccc vlan 10 interface fa0/1
 View Full Image
View Full Image
VLANs (Virtual LANs)
VLANs isolate broadcast traffic by logically segmenting the network. Each VLAN creates a separate Layer 2 broadcast domain.
⚠️ Note: Devices on different VLANs need routing (Router-on-a-Stick or Layer 3 Switch).
- Native VLAN: VLAN that carries untagged frames (typically VLAN 1)
- Voice VLAN: Used to separate voice traffic from data
Switch(config)# vlan 10 Switch(config-vlan)# name SALES
 View Full Image
View Full Image
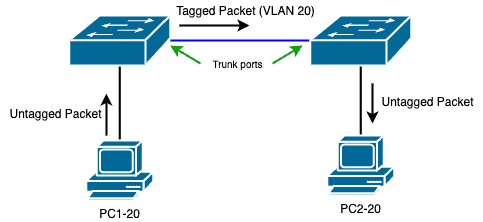
Trunking and 802.1Q
Trunk ports allow multiple VLANs across a single physical link using tags. 802.1Q inserts a VLAN tag inside Ethernet frames.
📘 Real-World Tip: Always set native VLAN to unused ID for better security.
Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q Switch(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
 View Full Image
View Full Image
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol)
STP prevents broadcast loops in Layer 2 networks. It elects a root bridge and places redundant links in a blocking state to break loops.
- BPDU: Bridge Protocol Data Units used for STP communication
- Port States: Listening, Learning, Forwarding, Blocking
Switch(config)# spanning-tree vlan 1 priority 4096
✅ Quick Fact: Lower bridge priority increases the chance of becoming root bridge.
 View Full Image
View Full Image
EtherChannel
EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant, aggregated links using PAgP or LACP. It avoids STP blocking and increases bandwidth.
Switch(config)# interface range fa0/1 - 2 Switch(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode active
🔍 Exam Tip: LACP is open-standard (active/passive); PAgP is Cisco proprietary (desirable/auto).
 View Full Image
View Full Image
Summary Table
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| VLAN | Separates broadcast domains |
| Trunking | Transports multiple VLANs via tagging (802.1Q) |
| STP | Prevents Layer 2 loops |
| EtherChannel | Aggregates links to increase bandwidth |