CCNA Chapter 4: IP Services
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
DHCP automates IP address assignment, reducing manual configuration. It uses the DORA process: Discover, Offer, Request, Acknowledge.
Exam Tip: Ensure devices receive the correct gateway and DNS with DHCP options.
Router(config)# ip dhcp pool SALES Router(dhcp-config)# network 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 Router(dhcp-config)# default-router 192.168.10.1 Router(dhcp-config)# dns-server 8.8.8.8
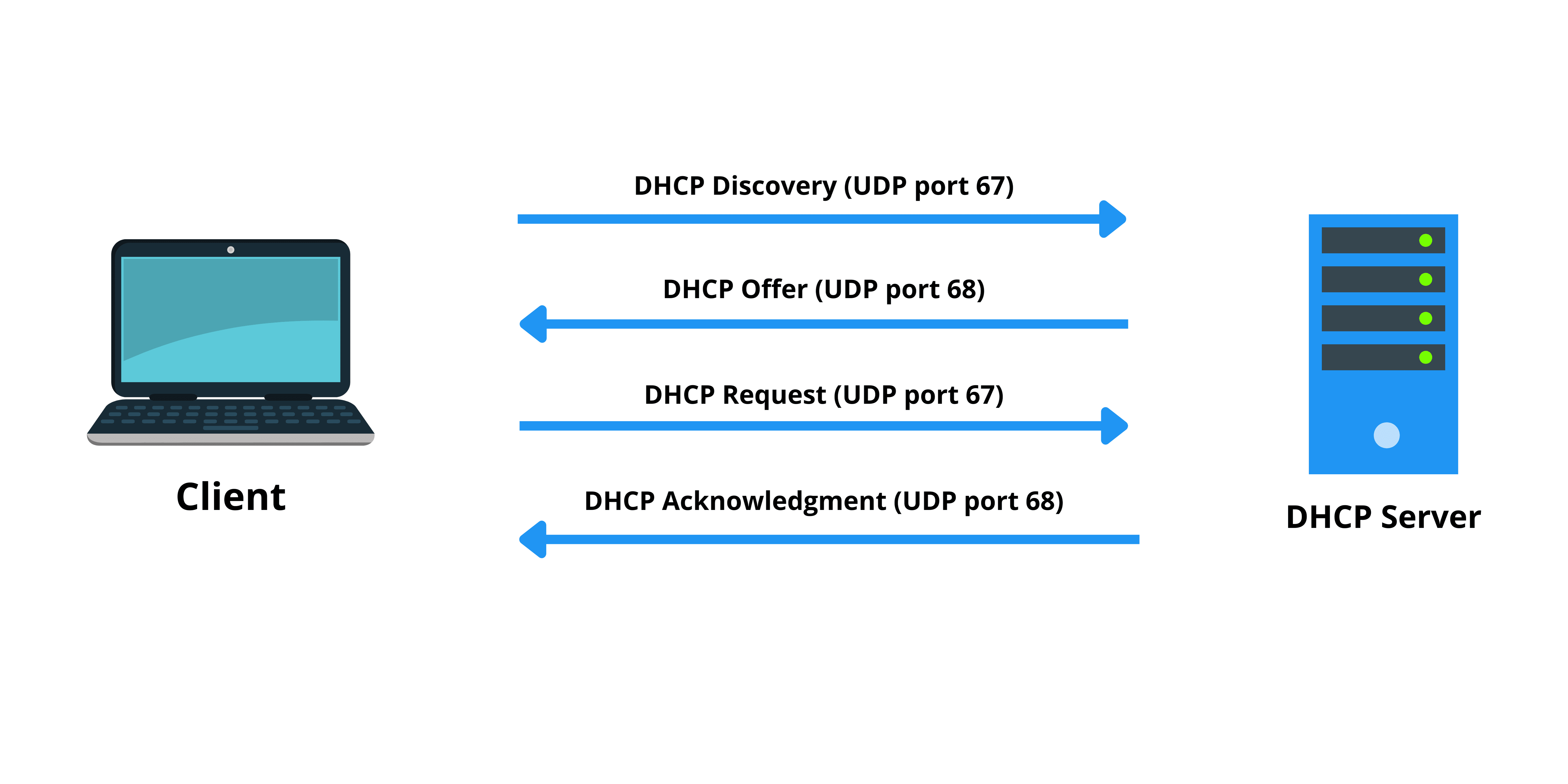 View Full Image
View Full Image
DNS (Domain Name System)
DNS translates human-friendly domain names into IP addresses. This service is essential for internet browsing and service discovery.
Security Note: DNS spoofing can mislead users to fake websites.
Router(config)# ip name-server 8.8.8.8
 View Full Image
View Full Image
NAT (Network Address Translation)
NAT allows private IP addresses to communicate with the internet by translating them to a public IP. Three types exist: Static, Dynamic, and PAT (Port Address Translation).
Real-World Tip: PAT conserves IP addresses and is the most common in home and office networks.
ip nat inside source list 1 interface g0/1 overload access-list 1 permit 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255
QoS (Quality of Service)
QoS manages bandwidth by prioritizing traffic like voice and video. It ensures critical applications perform well during congestion.
- Classification: Marking packets (e.g., DSCP)
- Congestion Management: Queuing mechanisms like LLQ, CBWFQ
- Policing/Shaping: Control traffic rates
class-map VOICE match ip dscp ef policy-map QOS-POLICY class VOICE priority 512 interface g0/1 service-policy output QOS-POLICY
Quick Fact: DSCP EF (Expedited Forwarding) is commonly used for voice traffic.
NTP (Network Time Protocol)
NTP synchronizes device clocks over a network. Accurate time is critical for logs, certificates, and troubleshooting.
Router(config)# ntp server 192.168.1.100 Router(config)# clock timezone MYT 8
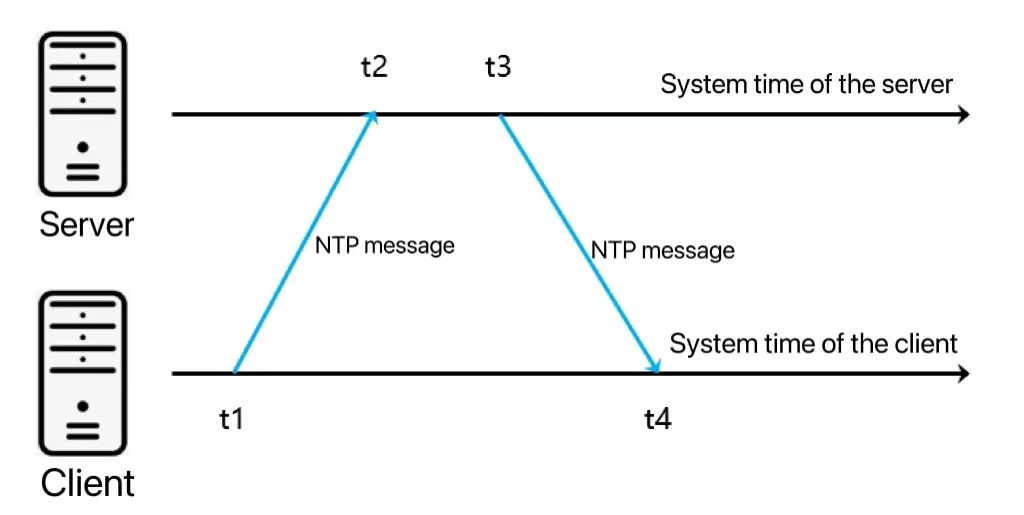 View Full Image
View Full Image
Summary Table
| Service | Description |
|---|---|
| DHCP | Automatically assigns IP configuration to clients |
| DNS | Resolves domain names to IP addresses |
| NAT | Translates private IPs to public for internet access |
| QoS | Prioritizes traffic to manage bandwidth and reduce latency |
| NTP | Synchronizes time across network devices |