CCNP Chapter 1: Cybersecurity Fundamentals
Cybersecurity vs. Information Security
Cybersecurity extends traditional Information Security by including real-time threat intelligence, OT/ICS protection, and more dynamic, proactive defense measures.
- Information Security: Focuses on data protection (CIA Triad)
- Cybersecurity: Includes network protection, endpoint detection, and threat response
 View Full Image
View Full Image
Security Frameworks
Frameworks guide best practices and standardization. Common ones include:
- NIST: U.S. cybersecurity framework based on identify, protect, detect, respond, recover
- ISO/IEC 27001: International ISMS (Information Security Management System)
- CIS Controls: Prioritized defensive controls
- MITRE ATT&CK: Adversarial tactics and techniques knowledge base
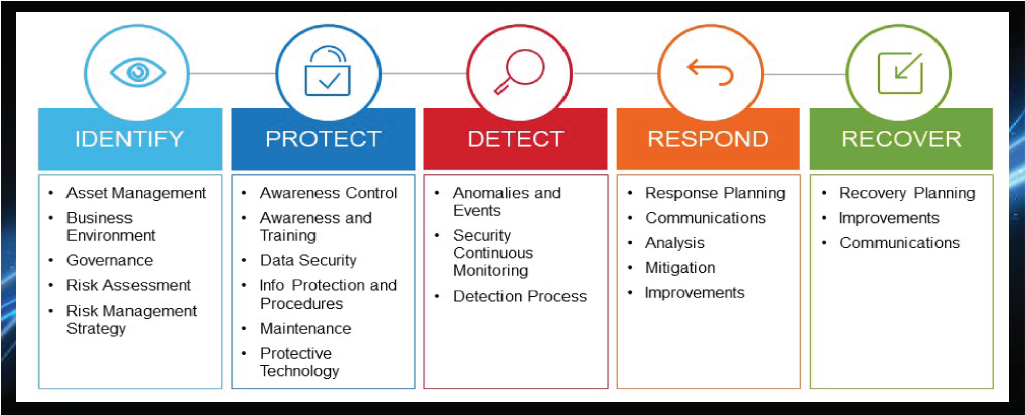 View Full Image
View Full Image
CIA Triad
The foundational principle of security:
- Confidentiality: Preventing unauthorized access to data
- Integrity: Ensuring accuracy and reliability of data
- Availability: Ensuring data and systems are accessible when needed
Common Threats
Cyber threats include:
- APTs: Advanced persistent threats targeting organizations for extended periods
- Zero-days: Exploits not yet known to vendors
- Insider threats: Internal actors misusing access
- Phishing: Social engineering via deceptive emails
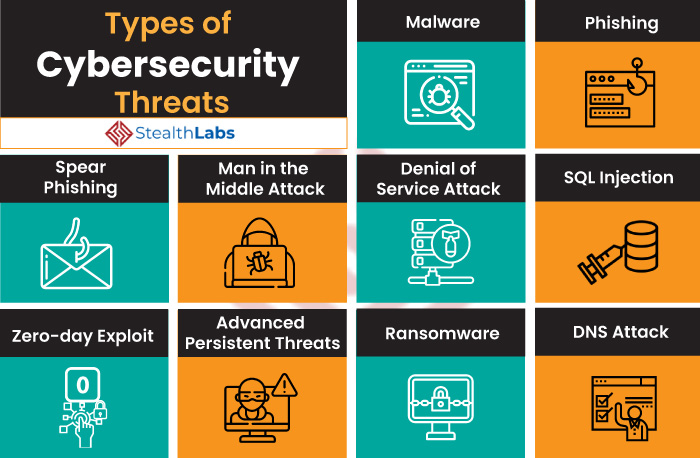 View Full Image
View Full Image
Incident Response Lifecycle
Defined by NIST SP 800-61:
- Preparation
- Detection and Analysis
- Containment, Eradication, and Recovery
- Post-Incident Activities
 View Full Image
View Full Image